Welcome to LED Learning Center
What is an LED?
What are Surface Mount LEDs?
What is a DIP LED?

A light emitting diode (LED) is a tiny, electronic semiconductor that converts electric energy into visible light. The chemical compound used within an LED determines its color, brightness and power efficiency.
Unlike incandescent lamps, LEDs have no filaments that can burn out or fail.
What is a DIP LED?
What are Surface Mount LEDs?
What is a DIP LED?

DIP LEDs are mounted with leads protruding through the circuit board and appear to stand taller. Each LED is a single-color die of either red, green or blue.
What are Surface Mount LEDs?
What are Surface Mount LEDs?
What is COB LED & why is it bettter?

Surface Mount Devices, or SMD for short, refers to the LED lead frame mounting method. LEDs are mounted to the surface of the circuit board. The SMD contains red, green and blue die.
What is COB LED & why is it bettter?
What is COB LED & why is it bettter?

COB stands for Chip on Board. It is a method of encapsulating LED chips in which arrays of LED chips are bonded directly to a printed circuit board (PCB), and then covered by epoxy.
Unlike SMD LEDs, each chip does not have its own lead frame, bonding wire and packaging. This means that the chips can be mounted extremely closely together on the PCB, paving the way for ultra-high-definition LED screens.
What is a pixel?
What is an LED panel?
Pixels, short for picture elements, are points of light that illuminate to form letters, words, graphics, animations and video images. A pixel can be made up of a single LED, multiple LEDs of the same color or multiple LEDs of different colors. They are the smallest elements of the electronics display system that can be individually controlled and turned off or on at various brightness levels.
What is an LED panel?
What is an LED panel?

An LED panel is a flat display, which uses arrays of light-emitting diodes (LED) as pixels for a video wall. The modular design feature of the LED panel enables us to build an unlimited video wall.
Their brightness allows them to be used outdoors in store signs and billboards. They have also become commonly used in control rooms and boardrooms, replacing conventional LCD/DLP/PDP video walls.
What is an LED module?

LED panels are made up of LED modules that form the building blocks of the LED wall. Rows of modules line together to arrange the LED panel in different variations depending on their product, market and purpose.
Each module could be replaced easily if any LED of the panel is malfunction.
What is an LED Video Wall?

In electronic visual displays, the primary colors normally used are red, green and blue. The primary colors used in the LED displays are typically saturated red, green and blue LED.
There is a solid theory behind it: the RGB color model, an additive color model in which red, green and blue light are added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors.
LED display equipped with the RGB LEDs is called an LED videwall or, to some people, a full colour LED display.
What is a DIP LED display?
What is an SMD LED display?
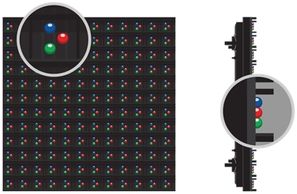
DIP LED displays use an array of DIP LEDs as pixels. DIP LEDs use a reflector cup and an epoxy lens package. This combination as well as the type of die used, plays a role in determining the elliptical viewing cone produced. A DIP LED's reflector cup focuses the light emitted by the die into a specific viewing area.
Benefits of DIP LED display
- Brighter than SMD LED dsiplay
- Black matte finish reduces reflection
- Louvers deflect sunlight for higher contrast
- Optimized for moderate to longer viewing distance
What is an SMD LED display?
What are viewing distance and pixel pitch?
What is an SMD LED display?

An SMD LED display is equipped with SMD LEDs. The total light emitted of the SMD LED isn't concentrated in a focused area since it does not have directional reflector cups. Instead light disperses evenly across both horizontal and vertical angles, providing wider viewing angles. This makes SMD LEDs an excellent choice for most indoor applications as well as some tighter pitch outdoor applications.
Benefits of SMD LED display
- Wider viewing angle than DIP one
- No color shift at extreme angles
- Outstanding color blending at short viewing distance
What are viewing distance and pixel pitch?
What are viewing distance and pixel pitch?
What are viewing distance and pixel pitch?
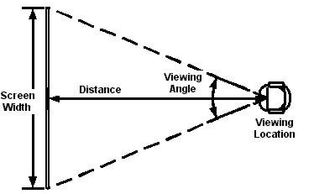
Viewing distances are calculated based on the display type and the distance from the display. Each display will have a minimum and a maximum viewing distance that may vary based on application and intended use.
Pixel pitch is the distance between the center of an LED and the LED next to it. Pixel pitch relates to the resolution of an LED display. The shorter the pixel pitch, the higher the resolution.
It is widely accepted in China that the pixel pitch of an LED display is taken as the minimum viewing distance, for instance, the mini. viewing distance of a P4 (pixel pitch 4mm) LED display is 4 m, which is not correct.
What are viewling angles?
What are viewing distance and pixel pitch?
What are viewing distance and pixel pitch?

In display technology parlance, viewing angle is the maximum angle at which an LED dispslay can be viewed with acceptable visual performance. LEDs are measured so that the line along half the viewing-angle from directly forward is half the brightness as at directly forward.
When choosing a display, consider where it will be installed and the angle at which the display will be viewed. Image quality will be at it's best within the viewing cone of the display - where your primary intended audience should be located. Readability angle or viewing area will exceed the optimum viewing angle depending on site-specific circumstances and ambient light conditions.
How does an LED display work?
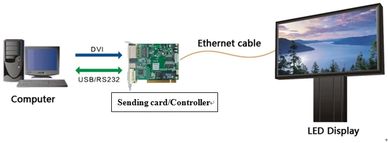
An LED dsiplay works with a controller (a hardware, sometimes known as sending card) and a PC-based software and the content of the LED screen is published via the software is called a synchronous system, while an asychronous system is without the PC and the content is saved in a U-disck or CF card and is a plug & play solution. Normally, the asychronous system is suitable for a limited size of LED display, especially for the LED message display.
What is a video processor?

A video scaler/processor is a system which converts video signals from one display resolution to another; typically, scalers are used to convert a signal from a lower resolution to a higher resolution or converting from high to low resolution.
You need the video processor if you want to utilize different video resources, like Camera system, DVD Player, Set Top Box, etc.
What is a cloud-based publishing system?
What is a cloud-based publishing system?
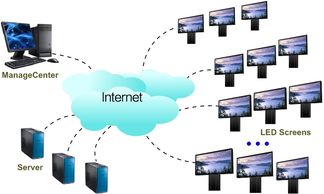
We together with our partner Novastar proudly present the VNNOX system to the market, a cloud-based publishing LED control system, which features 1) remote Control, 2) remote publishing, 3) playlist scheduling & saving, 4) IOS compatible, etc.
The VNNOX system is a premium solution for adverting company.
What is colour depth?
What is LED calibration?
What is a cloud-based publishing system?

Colour depth (Most LED suppliers mistakenly state it as greyscale) also known as bit depth, is either the number of bits used to indicate the color of a single pixel, in a bitmapped image or video frame buffer, or the number of bits used for each color component of a single pixel. For consumer video standards, the bit depth specifies the number of bits used for each color component.The higher the bit, the finer the image.
But color depth is only one aspect of color representation, expressing how finely levels of color can be expressed (a.k.a. color precision); the other aspect is how broad a range of colors can be expressed (the gamut).
What is refresh rate?
What is LED calibration?
What is LED calibration?

The refresh rate is the number of times in a second that a display hardware updates its buffer. This is distinct from the measure of frame rate in that the refresh rate includes the repeated drawing of identical frames, while frame rate measures how often a video source can feed an entire frame of new data to a display.
Within certain range, increasing the refresh rate decreases flickering, thereby reducing eye strain. However, if a refresh rate is specified that is beyond what is recommended for the display, damage to the display can occur.
The left image is an image with low refresh rate, while the right one is of high refresh rate.
What is LED calibration?
What is LED calibration?
What is LED calibration?

The wavelength of the LED, and thus its colour, depends on the band gap energy of the materials forming the p-n junction. (LED consists of a chip of semiconducting material doped with impurities to create a p-n junction.) Different band gaps deteriorate the colour uniformity of the LED display. The aim of the colour calibration is to measure and/or adjust the colour response of the LED display to a known state, and thus enhance the colour uniformity.
The LED calibration system features of a video calibration software: software that receives the signals from the color analyzer and displays the data in numerical format which is interpreted in a human interface in the form of real-time charts and graphs. Calibrators use this information to guide decisions about how to properly adjust the displays.
Copyright © 2016 - 2025 VividDots - All Rights Reserved.
Trust The Professional.